The supply chain is the foundation of e-commerce logistics. Its digitalization is not just a concept, but relies on tools and technologies capable of transforming flow management. From inventory tracking to final shipment, each step can be optimized thanks to digital and scalable solutions.

The advantages and disadvantages of logistics digitalization
The advantages and disadvantages of logistics digitalization Digitization is profoundly transforming the e-commerce supply chain. Companies benefit from real-time visibility of their flows, from goods receipt to final delivery. This traceability reduces errors, facilitates planning, and makes it possible to anticipate stockouts. Automating processes, whether picking, packaging, or shipment tracking, significantly improves productivity and reduces operational costs.
However, this evolution requires initial investments, particularly in the acquisition of specialized software and team training. It also implies a greater reliance on digital systems, which requires the implementation of a reliable and secure infrastructure. However, these constraints remain limited compared to the benefits of a digitalized supply chain, capable of constantly adapting to demand.
Logistics without digital transformation: a brake on growth
A supply chain that remains based on manual processes quickly runs into its limits. Preparation times lengthen, inventory errors multiply, and logistics costs explode. Customers, for their part, do not benefit from accurate order tracking and see their confidence diminish. In a highly competitive market, a non-digitalized supply chain becomes a brake on growth and exposes the company to the risk of losing its competitiveness.
A digitalized supply chain with the right tools
Supply chain transformation begins with the integration of systems capable of providing complete, real-time visibility into flows. Software makes it possible to forecast demand, optimize supplies, and synchronize the entire supply chain.
For inventory and warehouse management, WMS (Warehouse Management Systems) provide intelligent automation. These solutions reduce errors, streamline picking, and improve the efficiency of logistics teams.
For order management, OMS (Order Management Systems) manage merchandise availability and shipping conditions in real time to respond to demand as quickly as possible.
In transportation, TMS (Transport Management Systems) provide real-time tracking and optimize routes. They also help reduce carbon footprints by choosing the most efficient transportation solutions.
E-commerce as a digitalization accelerator
E-commerce platforms must be directly connected to the supply chain to ensure a seamless customer experience. Solutions include connectors that integrate with WMS and TMS, creating a coherent digital ecosystem.
Centralizing information via ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) makes it possible to link online sales to logistics operations. This provides customers with real-time tracking of their orders, and the company improves responsiveness to fluctuations in demand.
Automated and Intelligent Fulfillment
Fulfillment becomes strategic when it leverages automation and integration technologies.
Modern warehouses integrate picking robots and intelligent conveyors, reducing order preparation time. Automated packaging systems optimize packaging, reducing transportation costs and environmental impact.
Finally, SaaS solutions facilitate multi-carrier management by centralizing labeling, tracking, and returns.These tools offer great flexibility and considerable time savings, both for small businesses and large organizations.
The Strategy for Moving Toward a Global Supply Chain
The transition to a digitalized supply chain and efficient fulfillment involves several stages:
- Audit of existing processes.
- Selecting appropriate solutions.
- Progressive integration and team training.
The goal is to create a fluid ecosystem capable of adapting to market changes.
In Switzerland, these solutions provide an advantage in terms of proximity and quality.
Internationally, the diversity of markets makes the use of interconnected platforms essential to ensure the adaptation and fluidity of flows.
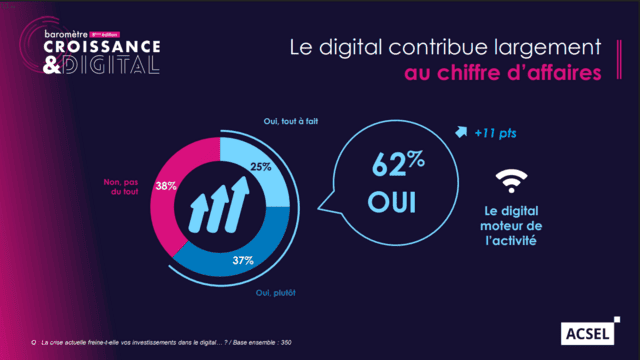
Digital policy and revenue. (Source: ACSEL)
How the essential tools transforming modern e-commerce logistics work
1. The OMS (Order Management System)
The OMS centralizes all orders from your various sales channels (website, marketplaces, stores) in a single interface. It analyzes inventory availability across all your distribution points in real time and automatically determines the best shipping location based on predefined rules: geographic proximity, transportation costs, and delivery times. The system then orchestrates the complete workflow: it sends the order to the correct warehouse or store, reserves inventory, manages delivery promises to the customer, handles changes or cancellations, and manages the returns process by automatically reintegrating products into available inventory.
2. The TMS (Transport Management System)
The TMS functions as a transportation optimization platform. Upon receipt of a shippable order, it automatically queries multiple carriers via their APIs to compare rates, delivery times, and service quality. Once the carrier is selected, it generates shipping labels, transmits tracking data, and tracks the package in real time using carrier feedback. The system automatically sends notifications to customers whenever the status changes. For fleets with their own fleets, it optimizes rounds by calculating routes that minimize distance and time while respecting delivery windows.
3. WMS (Warehouse Management System)
The WMS is the system that manages all warehouse operations. It works by automatically assigning an optimal location to each product received. When an order arrives, the system calculates the shortest route for the picker. It scans each item to verify compliance and instantly updates available inventory. The WMS also manages internal movements, replenishment of picking areas, and generates real-time performance dashboards.
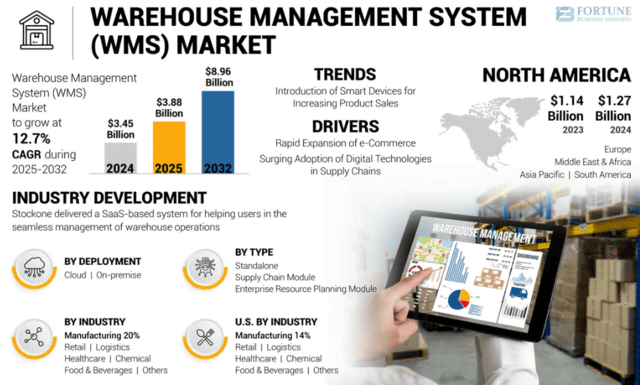
(source : Fortune Business)
4. ERP: The Company's Central Nervous System
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) functions like the central nervous system, connecting and synchronizing all of a company's departments. It centralizes all information in a single database: finance, accounting, human resources, purchasing, sales, and inventory. When an order is validated in the sales module, the ERP automatically triggers a chain of reactions: it reserves the stock, generates an invoice, updates the accounting system, adjusts cash flow forecasts, and can even trigger a purchase order if the stock level falls below the reorder threshold. The system ensures real-time data consistency across all modules.
5. Robotic Automation Solutions
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) tools work by recording and then automatically reproducing repetitive computer tasks: data extraction, form filling, document generation. Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) use sensors and cameras to map the warehouse, then move autonomously, avoiding obstacles, to transport goods or pallets from point A to point B.
6. AI and Analytics Platforms
These solutions first collect data from your various systems (sales history, inventory, weather, promotions, events). Machine learning algorithms then identify patterns and correlations to build predictive models. For demand forecasting, the system analyzes historical trends, seasonality, and external factors to calculate expected volumes by product and period. Dashboards visualize these predictions and continuously compare forecasts to actuals, gradually refining the models.
7. IoT (Internet of Things) Solutions
RFID tags contain an electronic chip that emits a unique radio signal identifying the product. Antennas placed at strategic points (entry/exit gates, storage areas) capture these signals and transmit the information to the central system, which updates the location in real time. Temperature and humidity sensors, placed in packages or vehicles, continuously measure ambient conditions and transmit the data via cellular or satellite networks.
Conclusion
The supply chain is the foundation of e-commerce logistics, and its digitalization relies on concrete and proven tools. E-commerce accelerates its evolution by imposing standards of speed and transparency. Finally, fulfillment, supported by these technologies, transforms the customer experience and becomes a strategic asset.
By combining scalable digital solutions, companies create an agile and resilient supply chain capable of meeting the challenges of Switzerland and the international market.
Do you want to optimize your supply chain in Switzerland, digitalize your logistics processes, and benefit from agile and efficient fulfillment? Emaloja supports you with scalable digital solutions tailored to your needs and ambitions.
Commencez à écrire ici ...
Digitalization and e-commerce logistics: scalable solutions for a sustainable future